- CE Outcomes, LLC; Birmingham, AL
- Gilead Sciences Europe Limited, Uxbridge, UK
- Gilead Sciences Inc, Foster City, CA
Overview
One of the foremost challenges related to outcomes studies of continuing education (CE) is the inability to compare and aggregate outcomes results due to variances in the collected data. From differing target audiences, divergent learning objectives, and activities being assessed with unique questions and measurement scales, there are many reasons why outcomes data cannot be compared. To address this issue, CE Outcomes collaborated with Gilead Sciences during 2019 on the development of a standardized outcomes assessment tool with the goal of implementing the tool across Gilead Sciences supported educational activities occurring around the world.
Background
In order to develop a standardized tool that would be widely accepted, CE Outcomes collaborated with Gilead Sciences on a multi-phase, requirements-gathering approach to define the elements of the standardized evaluation tool that would be most beneficial. The objective of the standardized tool was to capture consistent metrics assessing participation, satisfaction, knowledge and competence outcomes across educational activities that were being implemented by Gilead Sciences around the world (outside of the United States).
Furthermore, the tool had to meet the following criteria:
- Be applicable across different educational formats and therapeutic focus areas
- Collect meaningful educational outcomes data
- Not create a burden on the learner
- Meet the expectations of Gilead stakeholders around the world
Ultimately, the data captured from the standardized tool had to allow for 1) comparison between individual educational activities to make decisions regarding future education and 2) aggregation of data to demonstrate the overall value and collective impact of educational efforts.
The multi-phase requirements-gathering approach to define the standard evaluation tool metrics included engaging Gilead stakeholders from around the world. More than 300 individuals were invited to provide input on the elements for inclusion in the tool, and over 90 responses were gathered and used to inform the development of the standard evaluation tool.
After several rounds of revisions and comments, the standardized evaluation tool was piloted in six educational activities. The two-page standardized tool that was developed includes questions to capture data related to the impact of education on practice, including key take-away learnings, planned changes to practice and anticipated barriers to implementing the educational objectives. Further, the tool gathers data on learner satisfaction with the relevance of content, scientific and clinical accuracy of content, and achievement of learning objectives. Additional refinements were made to the tool following the pilot, and by July 2019, the tool was disseminated across the company for use in educational activities supported by Gilead outside of the United States.
Adoption Challenges
One of the key challenges faced in the implementation of a standardized assessment tool was rapid and wide adoption. To help facilitate adoption, it was important to ensure that all parties involved recognize the value of collecting outcomes data in a format that is different than what was previously used. To overcome this challenge, internal champions and leadership buy-in were crucial. A network of 20 country-level and regional champions was identified to help promote adoption of the standardized evaluation tool. The champions participated in training and were equipped with resources and templates to support implementation. In addition, calls were regularly scheduled to review any concerns or feedback related to the standard evaluation form and process of implementation.
Further, Gilead leadership realized the value of obtaining consistent outcomes data to show educational efforts are focused effectively and in a cost-efficient manner. They recognized the power of data to ultimately demonstrate that meaningful healthcare provider education would achieve the goal of better patient care.
The Power of Standard Data
Each educational activity that used the standard tool has a templated report of outcomes metrics that provides a consistent approach to displaying the data results for each individual activity. However, the power of the data from the standardized tool lies in the ability to aggregate the data to compare results across activities or demonstrate aggregated impact across educational initiatives. To assist in these efforts, a master database was created to maintain the results from each activity evaluation, allowing for data to be reported and analyzed to compare individual activities within a therapeutic area, region or country. Further, the aggregated data can provide a demonstration of overall educational reach and impact across multiple activities within a therapeutic area, geographic region or learner type.
Below is an example of the type of data reporting that can be generated by aggregating data from educational activities occurring across different therapeutic areas and different countries. Note: This example is not actual aggregated data; the data has been de-identified for purposes of illustrating the type of reporting that is possible.
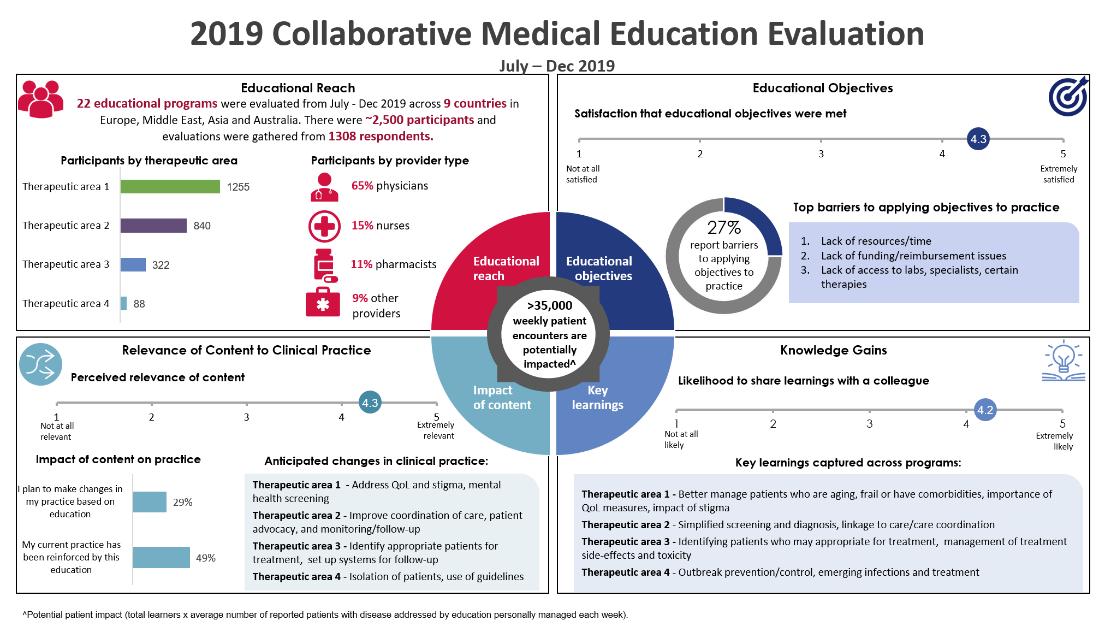
Summary
This standardized approach to gathering data allows for the demonstration of the collective impact of education, as well as an understanding of the comparative differences across individual activities. While the data associated with a standardized assessment tool can be powerful, one of the challenges with implementing a standardized evaluation tool is adoption. Gilead leadership and a network of champions who value outcomes data helped to speed the adoption of the tool. The standard evaluation tool is anticipated to be used widely in educational activities occurring during 2020 and 2021. The data collected will continue to demonstrate the value of education in meeting clinician educational needs and in aligning those needs with Gilead’s strategic goals. Further, the design of this approach will create the ability to assess whether adjustments are needed to ensure future educational activities are most effective and efficient in meeting company strategic goals.